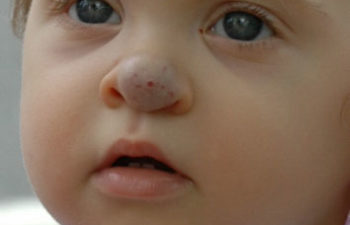
Birthmarks, also known as vascular anomalies, are common in newborn babies. Of these, approximately 90% will disappear within the first year of life. This is perhaps why many pediatric healthcare specialists advise parents to not have birthmarks evaluated by a vascular specialist. However, around 10% of children do develop birthmarks that can pose risks of complications. Of these, around half are infantile hemangiomas, which are benign tumors filled with blood.
Will My Child’s Hemangioma Go Away?
Beginning at around nine months of age, most hemangiomas begin involution, which is the process of shrinking. During this phase, blood vessels are replaced by a fibrous, fatty tissue. Those that shrink faster generally have more favorable results. By age two to three, it will become evident if your child’s hemangioma is shrinking quickly or slowly.
Those hemangiomas that complete the involution phase before age six typically require no treatment. Slower-shrinking hemangiomas that do not complete the process until after age six tend to leave residuum that may need treatment. Around half of all hemangiomas will require surgery to remove the fatty tissue mass that is left behind.
Do Hemangiomas Cause Problems?
It is impossible to determine if your child’s hemangioma will require treatment unless it is evaluated by a vascular specialist, like our team at The Vascular Birthmark Institute. Some hemangiomas are simply observed over time and pose no threats to health or aesthetics. Others can cause problems ranging from simple to severe.
In severe cases, your child’s hemangioma can pose problems with breathing, vision, eating, hearing or other basic functions. Some hemangiomas are internal and can interfere with the operation if vital organs, including the brain. These are often hard to detect, but they require immediate and serious treatment to prevent adverse consequences.
So When Should My Child’s Hemangioma Be Examined by a Specialist?
At the Vascular Birthmark Institute, we recommend that all visible hemangiomas be evaluated by a specialist as early as possible. Hemangiomas located on the neck or face should be evaluated immediately, as most of these will require treatment. Early and aggressive treatment can prevent future complications.
Also, consider that by between two to three years of age, a child develops a self-image. An obvious mark or facial disfigurement can pose problems in this regard. An early intervention could prevent any negative connotations by eliminating the cause for concern. Younger children also heal much faster and with less scarring than older children. Plus, more serious complications with hemangiomas can be avoided with early intervention.
Discuss your concerns first with your child’s pediatrician. They may be able to recommend a local specialist to evaluate your child’s hemangioma. If you still have concerns, or if your opinion differs from your local medical practitioner, remember that your child’s welfare is your responsibility. If you have questions or concerns about an infantile hemangioma, contact the team at the Vascular Birthmark Institute in New York. We will be glad to listen to your concerns and offer advice, or schedule a consultation and exam at our facility.
Posted on behalf of
Grand Park Building, 110 East 40 Street, Suite 501
New York, NY 10016
Phone: (212) 434-4050
FAX: (212) 434-4059
Email: info@vbiny.org
Monday-Friday: 8:30am-5pm